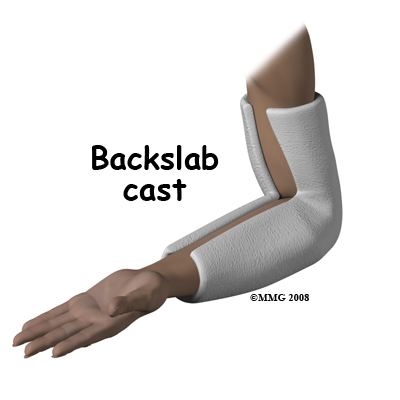
above elbow backslab
Radiohumeral joint located no associated fracture of ulna. Apply a layer of dry gauze bandage around the forearm to just below the elbow.

Forearm Volar Slab Splint The College Of Family Physicians Of Canada
Nondisplaced Mason Type I radial head fractures with full motion can be treated with a sling for comfort for 24-48 hours.
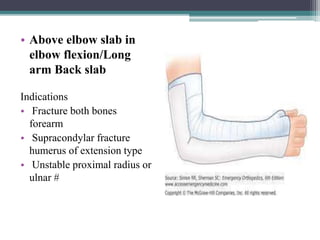
. Except for an all-Ottobock solution those components. Above elbow plaster backslab at 90 degrees flexion with Orthopaedic Fracture clinic follow up in 7-10 days. Radiohumeral joint subluxed or dislocated and or associated fracture of.
These include avulsion of the medial epicondyle fracture of the olecranon or proximal ulna. Associated elbow injuries occur in 50 of radial neck fractures. Cast related pressure injury.
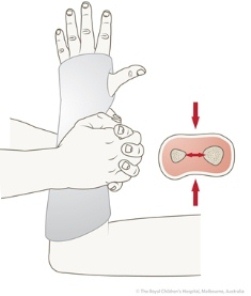
Place the slab longitudinally in position over limb fold any un-neat edges Mould by rubbing it smooth with flats of both palms and fingers Turn the ends of the webril back over the ends of the plaster Unroll the broad gauze bandage circumferentially around the limb to secure the plaster and free ends of webril roll layers should overlap by 50. Cut 2 triangles to cover the lateral and medial aspects of the elbow. The primary rationale for applying a splint or POP backslab is to stabilise the fracture prevent further injury and to hold the limb in the normal anatomical position.
They can also occur as a result of a posterior dislocation or reduction of the elbow joint. Above elbow backslab Post reduction XR. Olecranon fracture non-displaced and not involving the joint Radial neck fractures.
A slab equal to the above length is prepared dry as described above in 6 - 8 layers using a 15 cms POP roll The patients forearm is held in mid prone position with the elbow in 90 flexed position. On-line referral to virtual fracture clinic. Conservative immobilisation can be used for most fractures without above properties and also to stabilise fractures temporarily in case of delay before reductionfixation Splints and casts Splint non-circumferential immobiliser eg.
A randomized controlled trial comparing above-elbow posterior fiberglass slab and broad arm sling with collar and cuff immobilization without plaster slab was conducted at a childrens hospital emergency department. Above-elbow backslab for supracondylar fracture. Support us The Royal Childrens Hospital Melbourne.
MeSH terms Arm Injuries therapy Casts Surgical Fracture Fixation methods Fractures Bone therapy. Ensure elbow is well padded and padding overlaps itself by 25-50 with minimal creases. Squeeze out excess water smooth on a flat surface and apply along ulnar border of forearm.
These are useful for supracondylar fractures radial head fractures midshaft radius or u. Above Elbow Backslab and 34 backslab. Lower Limb Above-knee complete cast.
1 A posterior splint above elbow backslab may be applied in the acute setting but should not be used for more than a day or two. Below-elbow backslab fibreglass Below-elbow complete cast plaster of paris Splitting a below-elbow cast. Distal radius and ulnar fractures more than the ulnar styloid Distal radius fracture with significant angulation.
ORTHO ONCALL Olecranon fracture Neurovascular assessment Analgesia Above elbow backslab ORTHO ONCALL unless non-displaced or not surgical candidate VFC Radial headneck fractures If comminuted33 of articular surface15 angulation above elbow backslab - VFC Others DISCHARGE FROM ED WITH. POP plaster of paris physical plaster cast back-slab technique. More often physis or radial neck metaphysis More common in older teenagers.
Plaster backslab fibreglass backslab aluminiumwireheat-mouldable plastic splints. Below-knee backslab fibreglass Below-knee complete cast. Patients presenting with undisplaced supracondylar fractures were enrolled and reviewed after 2 weeks of immobilization.
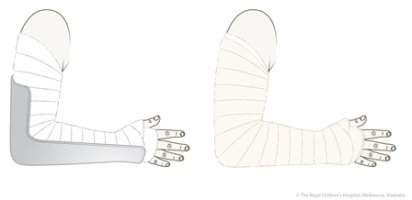
Radial neck fracture References Study of treatment methods for undisplaced supracondylar humeral fractures in children. Above Elbow backslab Extends from the middle of the upper arm to the point just proximal to the knuckles in the dorsum of the hand. Position patient Prepare slab of 8 layers of 15cm wide POP at minimum Length Middle of upper arm to just proximal to MCP joints Cut slits at elbow on either side to allow them to overlap Soft cotton roll applied with minimum 2.
How to apply the backslab in adults and paediatrics. Wrap softban down the arm completing 2 full rotations around the proximal aspect prior to advancing. Final checks prior to casting ensure the clinician is prepared to apply the correct cast to the correct limb and the manner directed by best practice.
Measure the slab on the unaffected arm- place the childs shoulder and elbow at 90 as pictured and measure from the upper limit to the lower limit. Splitting a below-knee cast. 5 sheets measured to length and doubled over Below Elbow SlabAbove Elbow Slab use 20cm plaster for BIG arms use 15 cm plaster for SMALL arms Below Knee SlabAbove Knee Slab back slab plus 5 layers for stirrups x 2.
A demonstration showing the application of an above elbow backslab. BELOW ELBOW BACKSLAB The plaster slab extends from a point about 5 cm below the top of the olecranon to the level just proximal to the knuckles in the dorsum of the hand and the distal crease in the palmar aspect. Unless youre willing to pay the premium price of complete modular bionic arms like the Atom Touch or the LUKE Arm which are worth the extra money we just wish more people could afford them those needing above-the-elbow bionic solutions will likely have to piece them together using multiple components.
Ice is applied during the first 24 hours. A well applied splint or POP backslab can provide safe and comfortable immobilisation of a fracture as part of the definitive management of an injury. Submerge the pre-prepared dry stirrup splint in water until bubbling stops then remove.
Collar cuff single or double loop Analgesia. Supracondylar fractures however Gartland I and II are usually placed in a collar and cuff Medial condyle fracture. Above elbow backslab.
Displaced unstable and combined Above elbow backslab at 90 degrees and consult. 2 Range of motion exercises should be started as early as possible. On-line referral to virtual fracture clinic.
The most common mechanism is a fall onto the outstretched arm with a valgus stress at the elbow. The EM3 education team demonstrates how to apply an above elbow backslab for patients followed by some helpful aftercare advice. Isolatedundisplaced Above elbow backslab at 90 degrees flexion and clinic.
Apply extra layers over prominent points Measure and Trim Plaster Slab Basic slab is 10 layers of plaster ie. It examines how above-elbow back slabs should be applied following fracture of the forearm elbow and distal humerus. Submerge the pre-prepared dry backslab in water until bubbling stops then remove.
Displaced fractures or 30 degrees angulation should be discussed with the Orthopaedic team for reduction.
Fracture Education Management Principles
Plaster Of Paris Synthetic Casts And Functional Cast Bracing

How To Apply An Above Elbow Backslab Youtube
Fracture Education Management Principles
Casting Above Elbow Back Slabs Mary Drozd And Colleagues Continue Their Series On Good Practice In Casting With A Review Of The Application Of Above Elbow Back Slabs Document Gale Academic Onefile
Above Elbow Backslab Living On The Edge
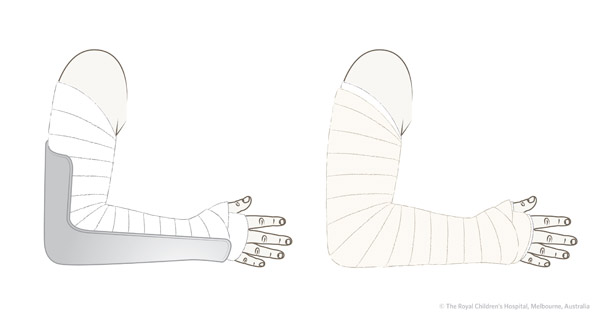
Clinical Practice Guidelines Radial Neck Fractures Emergency Department

How To Apply A Below Elbow Backslab Youtube

How To Apply A Below Elbow Backslab Youtube

Casting Above Elbow Back Slabs

Short Arm Cast The College Of Family Physicians Of Canada

The Tension Cord Plaster A Method Of Immobilising The Swollen Elbow Injury

Casting Above Elbow Back Slabs

Left Forearm In An Above Elbow Back Slab Anteroposterior And Lateral Download Scientific Diagram

Casting Below Elbow Back Slabs



Comments
Post a Comment